Skin parasites, though often overlooked, can be a significant source of discomfort and health issues. These parasites inhabit the skin, leading to various symptoms that can affect daily life. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking prompt treatment and preventing further complications. if you looking for parasitic infections treatment then you can take ivermectin doses for humans to treat parasitic infections. Here’s a comprehensive guide on identifying symptoms of skin parasites and what to look out for.
Types of Skin Parasites
Before diving into symptoms, it’s essential to understand the common types of skin parasites:
- Scabies Mites (Sarcoptes scabiei): Microscopic mites burrow into the skin, causing intense itching and rash. Take ivermectin 3 mg tablets to cure parasitic infections.
- Head Lice (Pediculus humanus capitis): Small insects that infest the scalp, causing itching and irritation.
- Body Lice (Pediculus humanus corporis): Similar to head lice, but found on the body, particularly in areas of clothing contact.
- Pubic Lice (Pthirus pubis): Commonly known as crab lice, these affect the pubic region but can also infest other coarse body hair.
- Fleas (Ctenocephalides spp.): External parasites that bite and feed on blood, often found in pets and the environment.
- Ticks (Ixodes spp.): These parasites attach to the skin to feed on blood, potentially transmitting diseases.
Common Symptoms
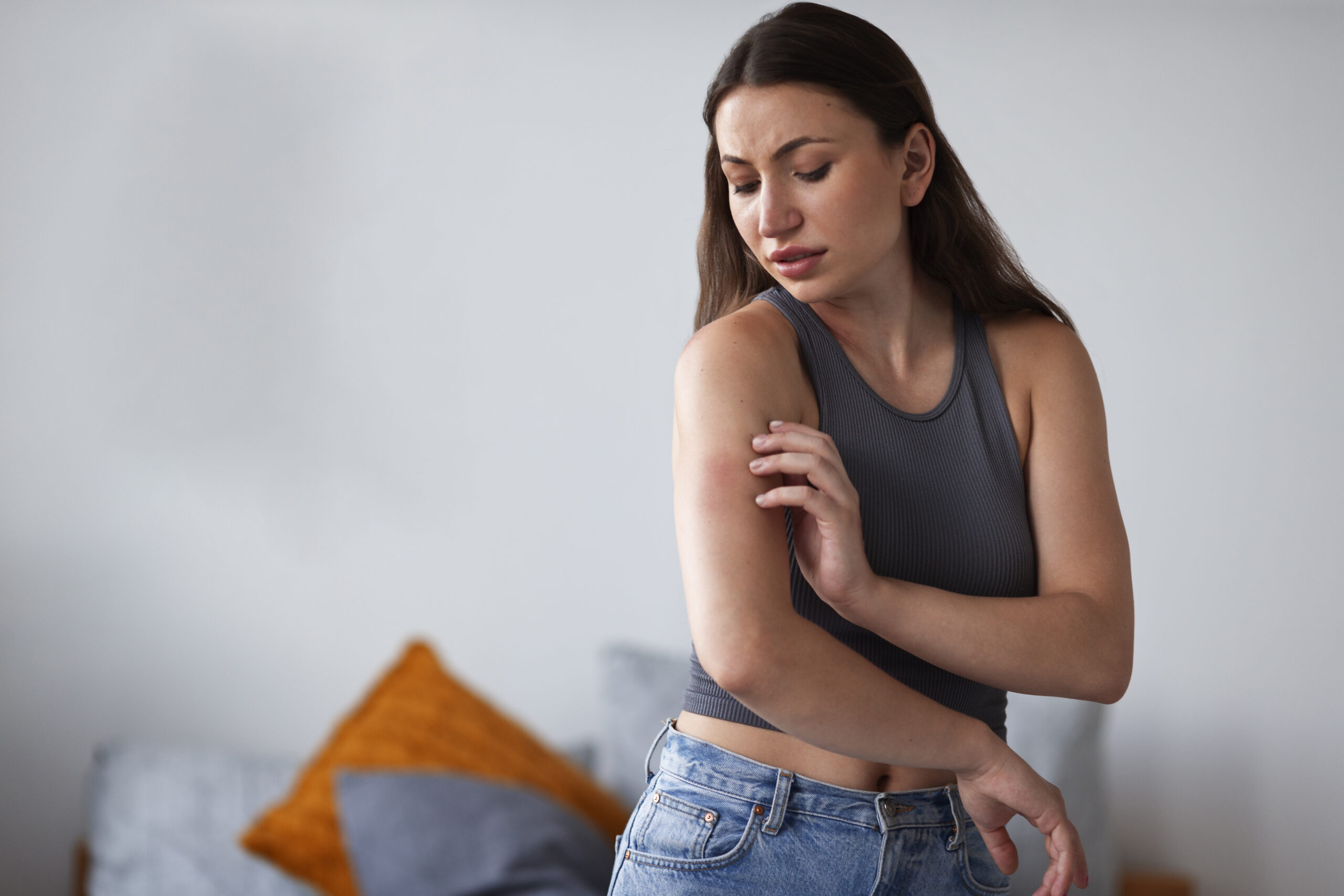
1. Itching and Irritation
One of the most prevalent symptoms of skin parasites is intense itching. This occurs as a result of the parasite’s feeding activities or the body’s allergic reaction to their saliva. For instance, scabies mites burrow into the skin, causing severe itching that often worsens at night. Similarly, lice bites lead to itching and discomfort, particularly in the scalp or pubic region.
2. Rash and Redness
A rash is another common symptom. In the case of scabies, the rash often appears as small red bumps, blisters, or pustules. The rash typically develops in areas where mites burrow, such as the wrists, elbows, and genital region. Lice bites also cause red, inflamed bumps, usually in clusters. Fleas can cause red, itchy welts, often found on the lower legs and ankles.
3. Sores and Skin Lesions
Scratching the itchy areas can lead to sores and open lesions. These secondary infections can occur as a result of scratching and can become severe if not treated properly. Infected sores may appear crusty, oozing, or swollen and may require medical attention to prevent further complications.
4. Visible Parasites
In some cases, you might actually see the parasites themselves. Head lice and nits (lice eggs) are often visible in the hair, while body lice can be seen on clothing or skin folds. Pubic lice are also visible in the pubic area. Fleas and ticks can be seen on the skin or fur of pets and can sometimes be spotted on humans.
5. Secondary Infections
Repeated scratching and irritation from skin parasites can lead to bacterial infections. Symptoms of a secondary infection may include increased redness, swelling, pus, and tenderness. This can complicate the primary infestation and may require additional medical treatment.
6. Abnormal Skin Texture
Chronic infestations can alter the texture of the skin. For example, repeated scratching due to scabies can lead to thickened, leathery skin in the affected areas. In severe cases, the skin may appear rough or discolored.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you have a skin parasite infestation, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can diagnose the condition through physical examination and, if necessary, microscopic examination of skin scrapings or hair samples.
Treatment typically involves:
- Topical Medications: For scabies, medications such as permethrin cream or sulfur ointment are commonly prescribed. Lice infestations are treated with special shampoos or lotions containing insecticides.
- Oral Medications: In some cases, oral medications may be needed, especially for severe infestations or if topical treatments are ineffective.
- Environmental Control: Treating the living environment is also essential. Washing bedding, clothing, and personal items in hot water can help eliminate parasites and prevent reinfestation.
- Medical Follow-Up: Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider ensures the infestation is fully eradicated and manages any secondary infections or complications.
Prevention
Preventing skin parasite infestations involves maintaining good personal hygiene and being aware of potential risks:
- Regular Cleaning: Regularly wash and clean clothing, bedding, and personal items.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Avoid sharing combs, brushes, or clothing with others, especially if they show signs of a skin parasite infestation.
- Pet Care: Regularly check and treat pets for fleas and ticks.
- Prompt Treatment: Seek prompt medical treatment if you suspect an infestation to prevent the spread to others and to mitigate symptoms.
Conclusion
Identifying symptoms of skin parasites early can significantly impact the effectiveness of treatment and overall health. Symptoms such as itching, rash, sores, and visible parasites should be promptly addressed with medical consultation. By understanding these symptoms and taking appropriate action, you can manage and prevent skin parasite infestations effectively.