Bacterial infections are common and can affect various parts of the body, ranging from minor skin irritations to severe conditions like pneumonia or meningitis. Understanding how bacterial infections are cured is crucial for maintaining good health. This guide covers the most effective methods to cure bacterial infections and how to prevent them from recurring.
Understanding Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections occur when harmful bacteria invade the body and multiply, causing symptoms such as fever, pain, swelling, and fatigue. These infections can be localized, affecting a specific area, or systemic, spreading throughout the body.
Diagnosis
Before treatment can begin, proper diagnosis is essential. Healthcare professionals typically diagnose bacterial infections through:
- Physical Examination: Checking symptoms and medical history.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests, urine tests, or cultures to identify the bacteria.
- Imaging: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs to assess the extent of the infection.
Treatment Options
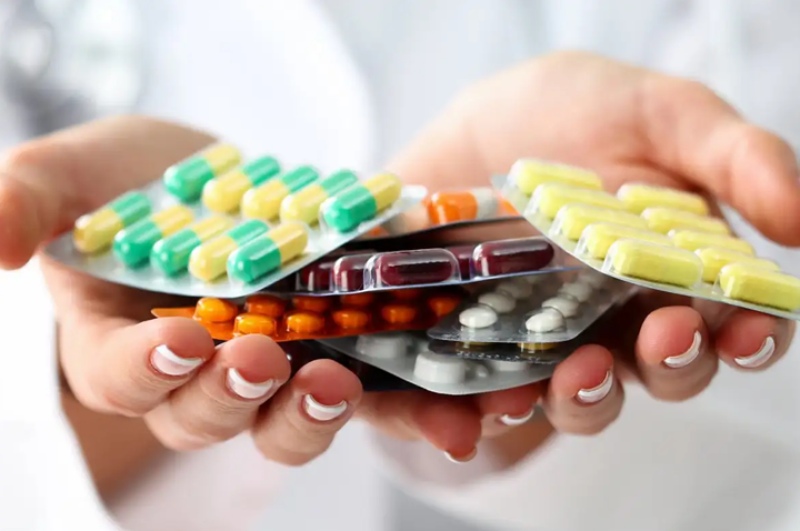
Once diagnosed, bacterial infections are primarily treated with antibiotics. However, the type of antibiotic and treatment duration depend on the specific bacteria causing the infection and the infection’s severity.
- Antibiotics
- Penicillins (e.g., Amoxicillin): Commonly used for skin infections, strep throat, and certain respiratory infections.
- Cephalosporins (e.g., Cephalexin): Used for pneumonia, kidney infections, and severe skin infections.
- Macrolides (e.g., Azithromycin): Buy azithromycin online that is effective for respiratory infections, sexually transmitted infections, and skin infections.
- Tetracyclines (e.g., Doxycycline): Buy doxycycline online is Used for acne, urinary tract infections, and respiratory infections.
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., Ciprofloxacin): Used for more severe infections like pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and gastrointestinal infections.
- Combination Therapy
- In some cases, a combination of antibiotics is necessary to tackle infections caused by multiple bacteria or resistant strains.
- Symptomatic Treatment
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to reduce pain and fever.
- Fluids and Rest: Essential for recovery and to help the body fight off the infection.
- Surgical Intervention
- For severe infections that cause abscesses or require the removal of infected tissues, surgery may be necessary.
Preventing Bacterial Infections
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of bacterial infections:
- Good Hygiene
- Wash hands regularly with soap and water.
- Keep wounds clean and covered until they heal.
- Vaccinations
- Stay up-to-date with recommended vaccinations to prevent diseases like whooping cough, tetanus, and pneumonia.
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get adequate sleep to boost the immune system.
- Safe Practices
- Practice safe food handling to avoid foodborne bacterial infections.
- Use antibiotics responsibly to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Conclusion
Bacterial infections can range from mild to life-threatening, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, they are usually curable. Antibiotics remain the cornerstone of treatment, but preventive measures play a crucial role in reducing the incidence of these infections. By maintaining good hygiene, staying vaccinated, and leading a healthy lifestyle, you can significantly lower your risk of bacterial infections.
For more personalized advice, consult with your healthcare provider, especially if you suspect you have a bacterial infection. Prompt treatment is essential for a full recovery and to prevent complications.